Schematic Images
Chapter II.1: Tear Film

Classical model of the precorneal tear film
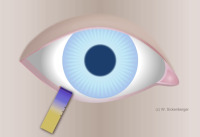
Schirmer test in the temporal third of the lower eyelid
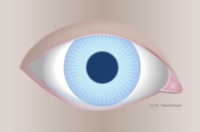
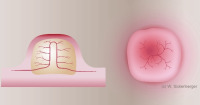
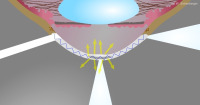
Tear meniscus
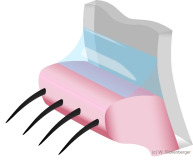
Tear meniscus cross-section
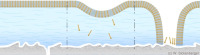
Schematic representation of a ruptured tear film

Dry patches

Regular target image of the Sutcliff ophthalmometer in the case of an intact tear film
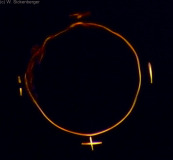
Distorted (anamorphic) Sutcliff ophthalmometer target image in the case of a ruptured tear film

Ideal image of the keratograph targets

Distorted (anamorphic) image of the keratograph targets

Strongly distorted (anamorphic) image of the keratography targets

Strongly distorted (anamorphic) image of the keratography targets

Tear film dynamics
LIPCOF Grade 0
LIPCOF Grade 1
LIPCOF Grade 2
LIPCOF Grade 3
Chapter II.2: Anterior segment findings
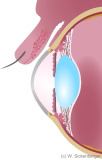
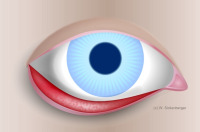
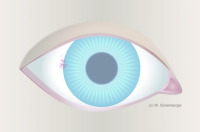
Anterior eye segment
Chapter II.3: Eyelids
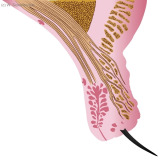
Cross-section of the upper eyelid
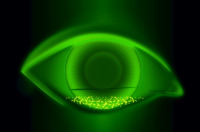
Incomplete closure of the eyelid
Chapter II.4: Conjunctiva
Anatomy of the conjunctiva
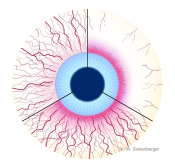
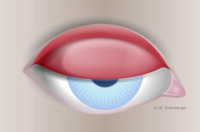
Overview of injection symptoms
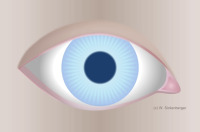
Bulbar redness - Grade 0
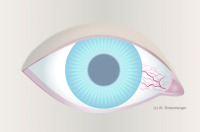
Bulbar redness - Grade 1, Isolated injection
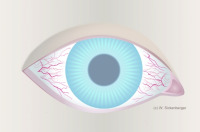
Bulbar redness - Gradе 2
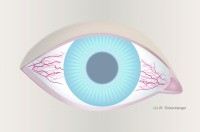
Bulbar redness - Grade 3 bulbar conjunctival injection: 3/9 o’clock redness due to dryness, often associated with 3/9 o’clock superficial punctate keratitis
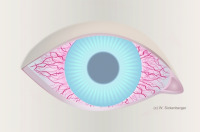
Bulbar redness - Gradе 4
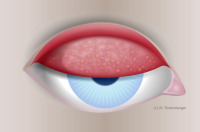
Everted upper eyelid with papillae
Papillae with central blood vessel
Everted lower eyelid with follicles
Follicle with superficial blood vessels

Grade 0 tarsal conjunctival injection - junctional papillae may be present
Grade 1 tarsal conjunctival injection – slight redness
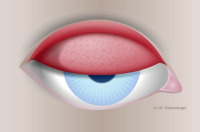
Grade 2 tarsal conjunctival injection – individual micropapillae (< 0.3 mm)
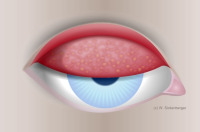
Grade 3 tarsal conjunctival injection – many macropapillae (0.3 – 1.0 mm)
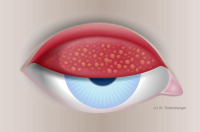
Grade 4 tarsal conjunctival injection – CLIPC, GPC (papillae > 1.0 mm)
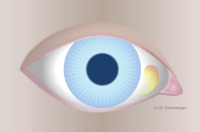
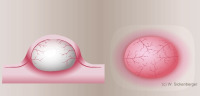
Pinguecula
Pterygium
Chapter II.5: Cornea
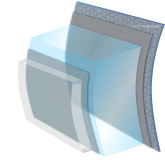
Illustration of the five layers of the cornea

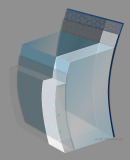
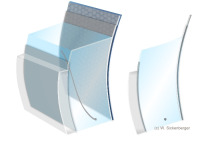
From parallelepiped to optical section
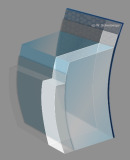
From parallelepiped to optical section
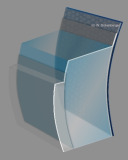
From parallelepiped to optical section
Sclerotic scatter
Optical section for examining the endothelium
Diffuse illumination
Direct focal illumination: optical plane
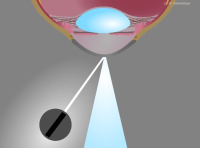
Direct focal illumination: optical cut
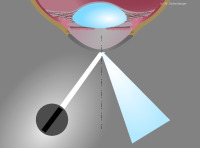
Reflective illumination
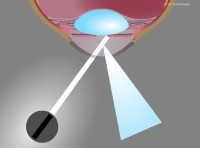
Conical bundle
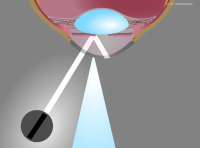
Indirect focal illumination
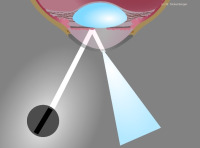
Retrograde illumination
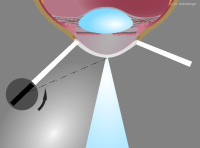
Sclerotic illumination

Illustration of various epithelial abnormalities
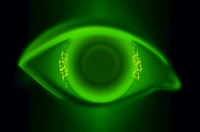
3/9 o’clock punctate keratitis
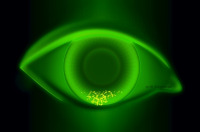
Localized punctate keratitis with desiccation
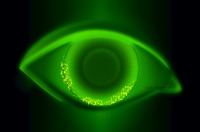
Superficial, diffuse punctate keratitis
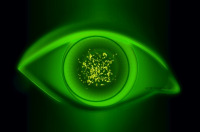
Central punctate keratitis
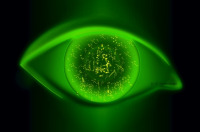
Deep, diffuse punctate keratitis
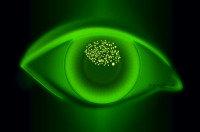
Air bubble dimple veiling
Impression from a foreign object

Erosion

Light-and-shadow phenomenon of microcysts and vacuoles
Location of microcysts and vacuoles

Stromal striae and Descemet’s folds
Location of the striae
Grade 1 vascularization
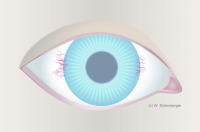
Grade 2 vascularization
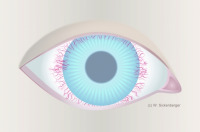
Grade 3 vascularization

Grade 4 vascularization
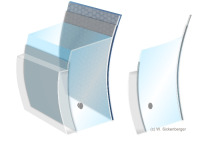
Location of infiltrates

AI - Asymptomatic infiltrates
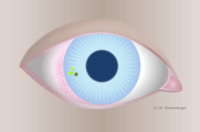
AIK - Asymptomatic infiltrative keratitis
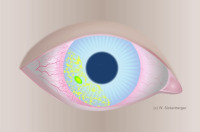
IK - Infiltrative Keratitis
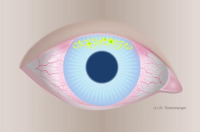
CLARE - Contact lens-induced acute red eye
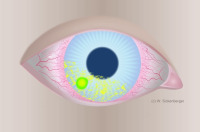
CLPU - Contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer
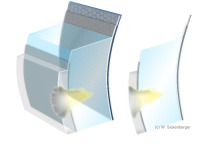
Corneal ulcer sectional views
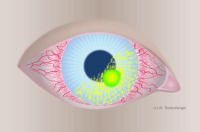
MK - Microbial keratitis

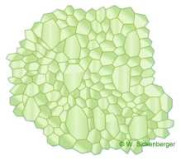
Hexagonal arrangement of endothelial cells
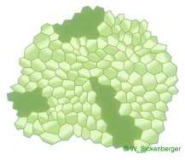
Polymegathism

Endothelial blebs
Cornea guttata
Location of precipitates
Chapter II.6: Anterior segment findings
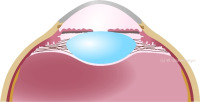
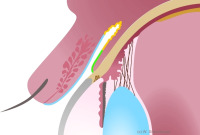
Cross-section through the anterior chamber
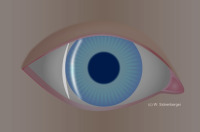
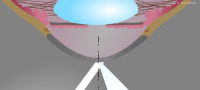
Appearance of the slit image in Van Herick’s method
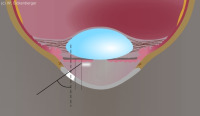
Measurement setup in Van Herick’s method
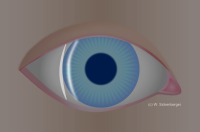
Van Herick’s Grade 4 - SC : ACA ratio = 1 : 1

Van Herick’s Grade 3 - SC : ACA ratio = 1 : ½
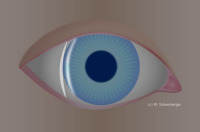
Van Herick’s Grade 2 - SC:ACA ratio = 1 : ¼

Van Herick’s Grade 1 - SC : ACA ratio = 1 : <¼
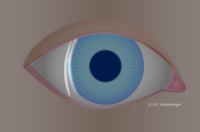
Van Herick’s Grade 0 - closed chamber angle
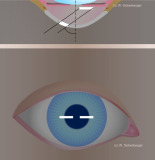
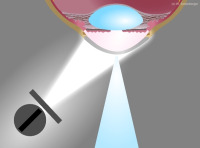
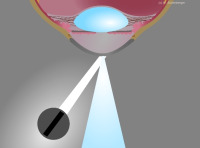
Illustration of Smith’s method – setup
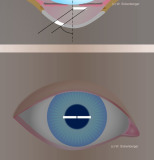
Illustration of Smith’s method - slit images in alignment
Chapter II.8: The Crystalline lens
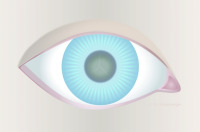
Frontal view
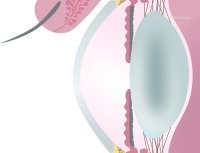
Cross-sectional side view
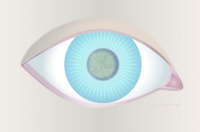
Frontal view
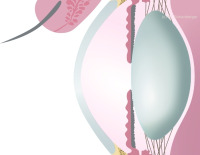
Cross-sectional side view
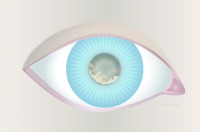
Frontal view
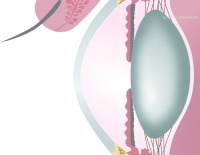
Cross-sectional side view
Chapter IV.4: Appendix (Contact lens terms)
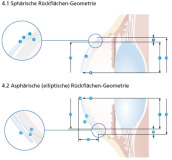
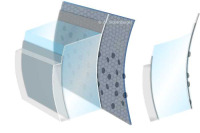
Contact lens terms